When we browse the internet, we rarely think of how it actually works. In order to access any type of data online, such as text, video, or even software – it has to be stored somewhere.
And we have two options for storing the internet data. One option is on-premise storage, which is basically a hard drive. It is a machine that has to be located somewhere, and therefore occupies space, uses a lot of energy, and requires expensive maintenance.
The other option is online storage, where data is stored “on the cloud.” This article is dedicated to what we call cloud computing.

Cloud Computing in a Nutshell
Cloud computing allows us to store and access any type of data online, avoiding physical hard drives. Of course, all of the data can be accessed through any device that has an internet connection – mobile phones, PCs, tablets, smartwatches, or others.
Thanks to cloud solutions, we are also able to process data online. Therefore, entire businesses function exclusively on the cloud, especially SaaS companies.
In essence, cloud computing separates the end user from the location of the data. Both can be anywhere on the planet now – or in space.
Cloud computing is a major trend because it is scalable, functional, and quite affordable. As such, it gives power to small and medium-sized companies to run complex software and IT architectures at a minimum cost.
Except for cost reduction, cloud computing boosts productivity, speed, and overall business efficiency.
Applications of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is just like the internet – it is a single facility that provides a huge variety of possibilities. Thus, cloud computing services can be applied for:
- Storing, managing, retrieving, and analyzing any type of data
- Emailing
- Live chats
- Creating, testing, and launching apps
- Audio and video streaming
And many, many more.
Cloud Computing Glossary
- The word “cloud” was connected to the concept of virtual space in the 1960s. Back then, the symbol of a cloud was used in charts and diagrams to refer to the internet. If you think it was very long ago, you are right. The internet wasn’t public until 1983, and the term “cloud computing” dates from the very early days of the internet, when it was still a prototype tested by the U.S. army.
- Cloud Migration – switching from on-premise to cloud computing. It is a major business trend at the moment because of the value it creates.
- Disaster Recovery – it is almost impossible to lose data on the cloud because cloud systems have backup and restoration abilities.
- Infrastructure as a Service – cloud computing even enables the outsourcing of physical computer infrastructure to businesses
- Software as a Service – ability to store and run apps online, thanks to cloud computing.
Forms of Cloud Computing
Depending on the purpose of using the Cloud, we categorize it in:
- Public Clouds – a cloud that hosts data and provides services to a large number of companies. In some cases, thousands of companies can use one cloud platform. This is usually a cheaper solution with more general settings. The companies pay the cloud provider, who is responsible for the maintenance, security, and scalability of the system. At the moment, around 91% of businesses use public clouds.
- Private Clouds – an in-house cloud that serves only one business or organization. They are highly customized and have above-average security protection. Therefore, they are costly and are usually used by large corporations and enterprises. These companies have IT teams that maintain, update, and set up the cloud system. Around 72% of businesses use this form of the cloud.
- Community Clouds – usually used by organizations such as hospitals or niche businesses. Several organizations may decide to share the same cloud because they have very specific needs and require similar settings.
- Hybrid Clouds – a combination of two or more of the previous three types. They are useful for organizations that need to consolidate and balance data from multiple resources. Around 69% of enterprises use hybrid clouds.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The numbers are clear on the matter: cloud computing is the future. According to Eurostat, cloud computing is already going mainstream in Europe.
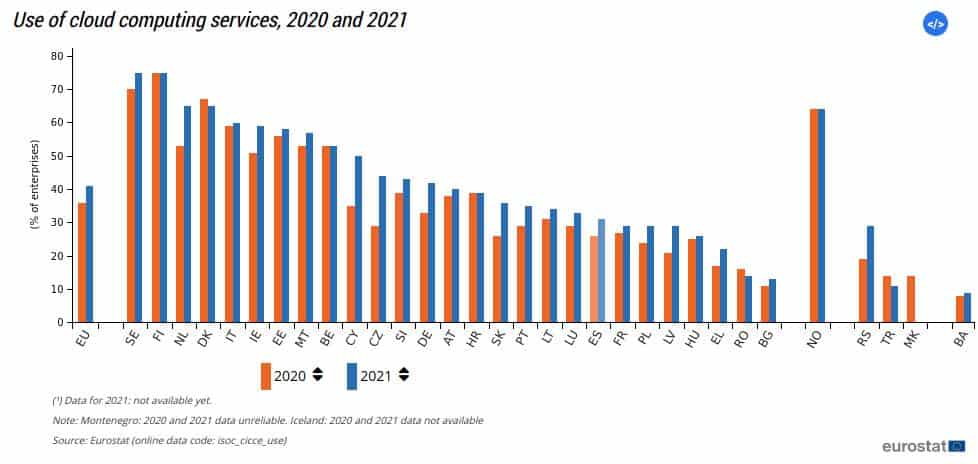
So what makes the cloud so appealing to businesses? Here are some major benefits:
- Quick Loading Time – with apps running on the cloud, the computing speed is a matter of seconds or even less than that. The cloud is not limited by the capacity of processors and graphic cards.
- Automatic Updates and Integration – it is very easy to test and update software and apps running from the cloud. Thus, companies making software can provide a better customer experience, and websites can run more smoothly with more functions.
- Efficiency – in simple words, cloud computing is working better, more quickly, and costs less. There is no equipment to buy and replace after a certain amount of time. In addition, much less electricity is used. Finally, much less personnel is required to maintain the systems.
- Data Security – cloud-based systems are promising in the domain of data security as well. Thanks to features like granular permissions, encryption, authentication, and federated roles that restrict access to sensitive data, preventing cybercrime and data breaches. When combined with the data protection implemented by businesses themselves, cloud systems are virtually impossible to steal.
- Easy scalability and customization – in a very dynamic market, businesses need hosting solutions that can quickly adapt to their specific needs. Therefore, cloud solutions are perfect for businesses with fluctuating demands and changing requirements. For example, startups might still be exploring the market, and by using cloud-based solutions, they can easily buy more or less space/services, depending on current needs. Thus, they avoid a lot of unnecessary expenses and become much more adaptive in the market.
- Collaboration – since communication among cloud devices and platforms is quick and easy, it makes lives much easier for developers and QA teams. Asking for and granting permissions has never been easier.
- Mobility – data stored on the cloud exists in the virtual space, and the only requirement to access it is to have the internet. Almost any device is able to access the cloud – phone, tablet, PC, and even game consoles, TVs, and smartwatches.

